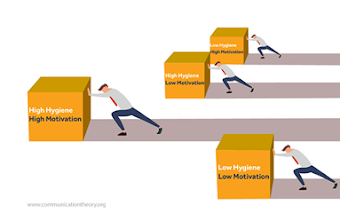
Figure 1: Different views between traditional motivation and
Herzberg’s two-factor theory.
(Chu
and Kuo, 2015)
According to Yousaf (2020) Motivation factors are,
- Advancement
- Work itself
- Possible of growth
- Responsibility
- Recognition
- Achievements
And the Hygiene factors are,
- Interpersonal relationship
- Salary
- Policies and administration
- Supervision
- Working condition
Table 1: Comparisons between the Two Factors of Herzberg’s Theory (Alshmemri, Shahwan-Akl and Maude, 2017)
In one of the organizations which I
worked for leading IT support services providing, the facilities provided by
the organization management,
Motivational factors
All employees get an extra amount of
money through an incentive scheme based on the department's performance. The
organization held the recognition program to motivate their employees such as
Engineer of the month, helpdesk coordinator of the month. It was a good working
environment to work and employees get the chance to implement their own ideas.
Hygiene Factors
It was introduced a new helpdesk system and helps to efficient all works. Supervisors have good relationships with their subordinates. It provides a good working condition and some other facilities such as food allowance, transport, medical coverage. For minor staff members get special school books for his/ her kids.
References:
Alshmemri,
M., Shahwan-Akl, L. and Maude, P. (2017) ‘Herzberg’s two-factor theory’, Life
Science Journal, 14(5), pp. 12–16. doi: 10.7537/marslsj140517.03.Keywords.
Chu, H.-C. and Kuo, T. Y. (2015) ‘Testing Herzberg’s
Two-Factor Theory in Educational Settings in Taiwan’, The Journal of Human
Resource and Adult Learning, 11(1), pp. 54–65. Available at: http://www.hraljournal.com/Page/10
HuichinChu&TsuiYangKuo.pdf.
Fauziah, W. et al. (2013) ‘HERZBERG ’ S TWO FACTORS
THEORY ON WORK MOTIVATION : DOES ITS WORK FOR TODAYS ENVIRONMENT ?’, 2(5), pp.
18–22.
John Adair (2009) ‘Frederick Herzberg: Hygiene Motivation
Theory thinker’, Chartered Management Institute, pp. 1–4. Available at:
https://www.bl.uk/people/frederick-herzberg.
Yousaf, S. (2020) ‘Dissection of Herzberg ’ s Two -Factor
Theory to Predict Job Satisfaction : Empirical Evidence from the
Telecommunication Industry of Pakistan’, 2(Spring), pp. 85–128.